TRACK 1: Inspiring Innovation in Formulation, Bioprocessing, and Drug Delivery
Category: Poster Abstract
(M0930-01-04) Macroporous Granular Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Controlled Oligonucleotide Delivery
Monday, May 5, 2025
9:30 AM - 10:30 AM ET

Angeliki Andrianopoulou, PharmD, MSc (she/her/hers)
PhD Student
University of Illinois Chicago
Chicago, Illinois, United States
Angeliki Andrianopoulou, PharmD, MSc (she/her/hers)
PhD Student
University of Illinois Chicago
Chicago, Illinois, United States- SA
Sonia Alavi
Ph.D. Candidate
Univeristy of Illinois Chicago
Chicago, Illinois, United States 
Richard Gemeinhart
Professor of Pharmaceutics and Bioengineering
University of Illinois Chicago
Chicago, Illinois, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Nucleic acid therapeutics, particularly short oligonucleotides (ODNs) such as microRNA, antisense ODNs, and siRNA, hold immense potential for treating a wide range of diseases, with several drugs recently gaining regulatory approval. However, efficient delivery of these fragile molecules remains a critical barrier to clinical translation. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have demonstrated success in enhancing ODN delivery, but further control over the dose and release timing is needed to maximize therapeutic efficacy. Incorporating ODN-loaded nanoparticles into hydrogels, forming nanocomposite hydrogels, offers a promising solution by improving drug stability and providing sustained delivery. However, traditional bulk hydrogels face challenges, such as simplified nanoparticle loading via direct soaking, achieving optimal porosity for high nanoparticle incorporation and precise control over nanoparticle release. To address these limitations, we present a novel macroporous granular hydrogel composed of densely packed interconnected microgels. This platform leverages a simple fabrication method and a one-step loading process for LNP-ODNs, enabling controlled and sustained release. Utilizing glutathione-conjugated poly(ethylene glycol) (GSH-PEG) hydrogels, we exploit electrostatic interactions between cationic nanoparticles and the hydrogel matrix to achieve precise delivery. This innovative approach demonstrates the potential for convenient, adaptable, and effective applications in ODN therapeutics.
Methods: A novel technique utilizing a confined T-junction connector was employed for microgel fabrication. The aqueous phase, consisting of 10% w/w 4-arm poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA, MW 20,000 Da), 55 mM glutathione (GSH), and a photoinitiator, was emulsified with the oil phase under controlled flow rates using syringe pumps. Droplets were polymerized upon collection or in-line within tubing upon UV exposure (20 mW/cm²). After extensive washing, granular hydrogels were formed by secondary crosslinking of the microgels, achieved through UV exposure following the addition of photoinitiator. Hydrogel swelling was performed in distilled water, and the hydrogel mass was recorded over time to monitor the swelling behavior. Cationic lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) were formulated via a one-step nanoprecipitation method using a T-junction system. LNPs were composed of DSPC, DMG-PEG- 2000, Cholesterol, DOTAP, and/or D-Lin-MC3-DMA. A 22-nucleotide single-stranded DNA was used as a model ODN and was either encapsulated or adsorbed in the LNPs to explore both incorporation strategies and their behavior in the granular hydrogel. ODN quantification was performed using the RiboGreen assay. LNPs at varying concentrations were incorporated into 35 μL granular hydrogels using a one-step soaking method for 24 hours. Release studies were conducted in PBS (pH 7.4) at 37°C. Samples were periodically withdrawn for quantification and replaced with fresh PBS to maintain sink conditions.
Results: Microgels exhibited spherical or conical shapes depending on whether they were polymerized upon collection or in-line, respectively. They had tunable sizes ranging from 10 μm to 700 μm, with a homogeneous size distribution and a coefficient of variation as low as 3%. The resulting granular hydrogels could be stored in aqueous solution at 4°C or lyophilized and rehydrated before application, offering a long shelf-life option. Freshly made granular hydrogels reached maximum swelling of 215 ± 21% within 6 hours, which decreased to 119 ± 22% after 48 hours, remaining stable for at least one week in water. Lyophilized hydrogels rehydrated within 24 hours. DOTAP-LNPs encapsulating ODNs had an average diameter of 99.9 ± 18.2 nm, a polydispersity index 0.19 ± 0.07 and a surface zeta potential of 10.7 ± 3.3 mV. Interestingly, ODN adsorption onto DOTAP-LNPs increased their size across various nitrogen-to-phosphate (N/P) ratios, while incorporating the ionizable lipid D-Lin-MC3-DMA enhanced LNP stability upon ODN adsorption. ODN encapsulation and adsorption efficiencies exceeded 95% across all formulations, except for adsorbed DOTAP-LNPs with an 82% adsorption efficiency at N/P 3. Adjusting the LNP stock concentration enabled control over the ODN amount loaded into the hydrogel. Release studies confirmed the delivery of intact nanoparticles maintaining incorporated ODN for over the period of 5 days, as verified by the RiboGreen assay, for both encapsulated and adsorbed ODN-LNPs. Lyophilized hydrogels demonstrated comparable delivery performance to hydrated hydrogels, highlighting their versatility for storage and application.
Conclusion: The development of an adaptable precipitation polymerization method for fabricating granular hydrogels, combined with a simple and efficient nanoparticle loading strategy, highlights the potential of GSH-PEG granular hydrogels for achieving controlled ODN delivery. This innovative GSH-PEG granular scaffold demonstrates significant promise for the versatile and sustained delivery of nanoparticles, particularly in topical applications.
References: 1. Daly, Andrew C., et al. "Hydrogel microparticles for biomedical applications." Nature Reviews Materials 5.1 (2020): 20-43.
2. Liu, Jiaping, et al. "Hydrogels for Nucleic Acid Drugs Delivery." Advanced Healthcare Materials 13.30 (2024): 2401895.
3. Andrianopoulou, Angeliki, et al. "Assessment of antibiotic release and antibacterial efficacy from pendant glutathione hydrogels using ex vivo porcine skin." Journal of Controlled Release 365 (2024): 936-949
Acknowledgements: We thank Sonia Alavi (UIC) for imaging with Keyence VHX6000 digital microscope. Figures were created with BioRender.com
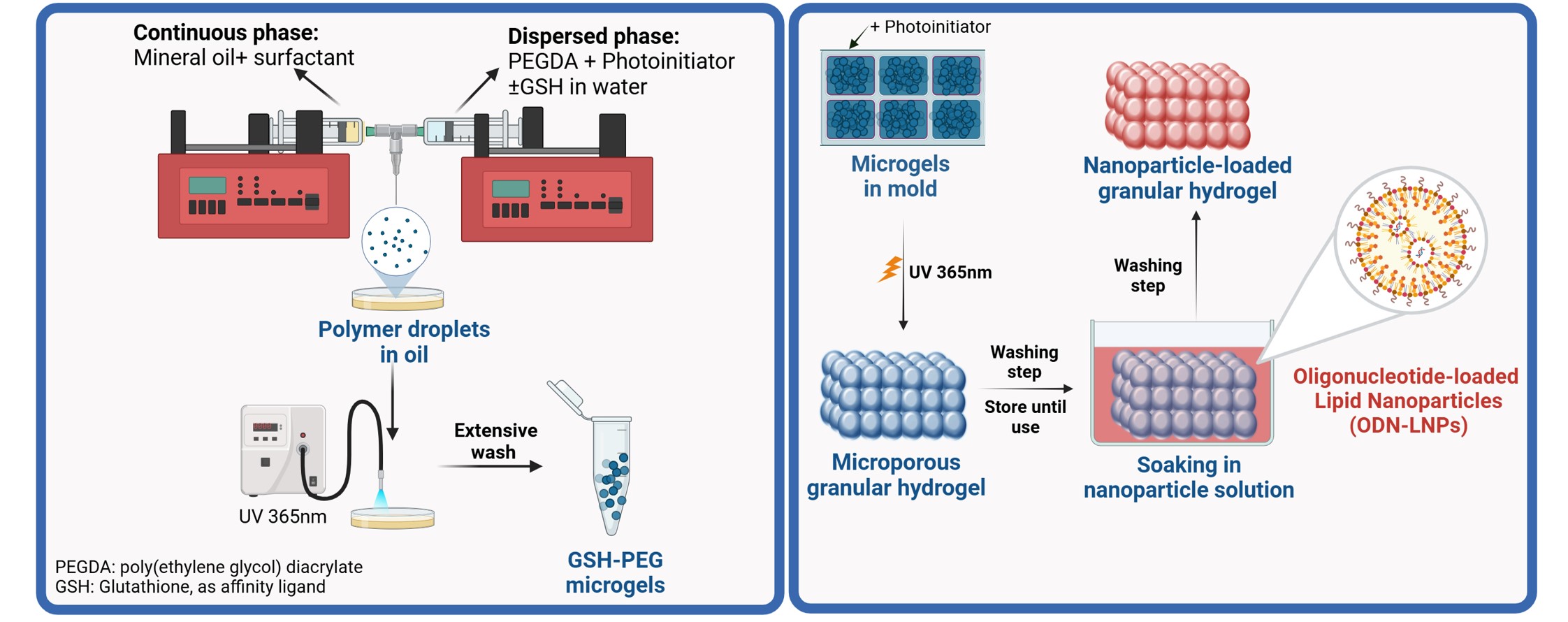 Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the microgel fabrication method and nanoparticle loading process in the granular hydrogel.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the microgel fabrication method and nanoparticle loading process in the granular hydrogel..jpg) Figure 2. (A) Microgel diameter (μm) as a function of varying the continuous flow rate (Qc) at constant dispersed flow rate of 1μL/min. Inset: microscope image of the produced microgels. Scale bar: 100μm. (B) Microgel diameter (μm) and coefficient of variation (%) as a function of total flow rate (μL/min). Data presented for three replicates, with measurements obtained from ten particles per replicate. (C) Microscopy image of hydrated (left) and lyophilized (right) granular hydrogel obtained with Keyence VHX6000 digital microscope. Scale bar: 500μm.
Figure 2. (A) Microgel diameter (μm) as a function of varying the continuous flow rate (Qc) at constant dispersed flow rate of 1μL/min. Inset: microscope image of the produced microgels. Scale bar: 100μm. (B) Microgel diameter (μm) and coefficient of variation (%) as a function of total flow rate (μL/min). Data presented for three replicates, with measurements obtained from ten particles per replicate. (C) Microscopy image of hydrated (left) and lyophilized (right) granular hydrogel obtained with Keyence VHX6000 digital microscope. Scale bar: 500μm.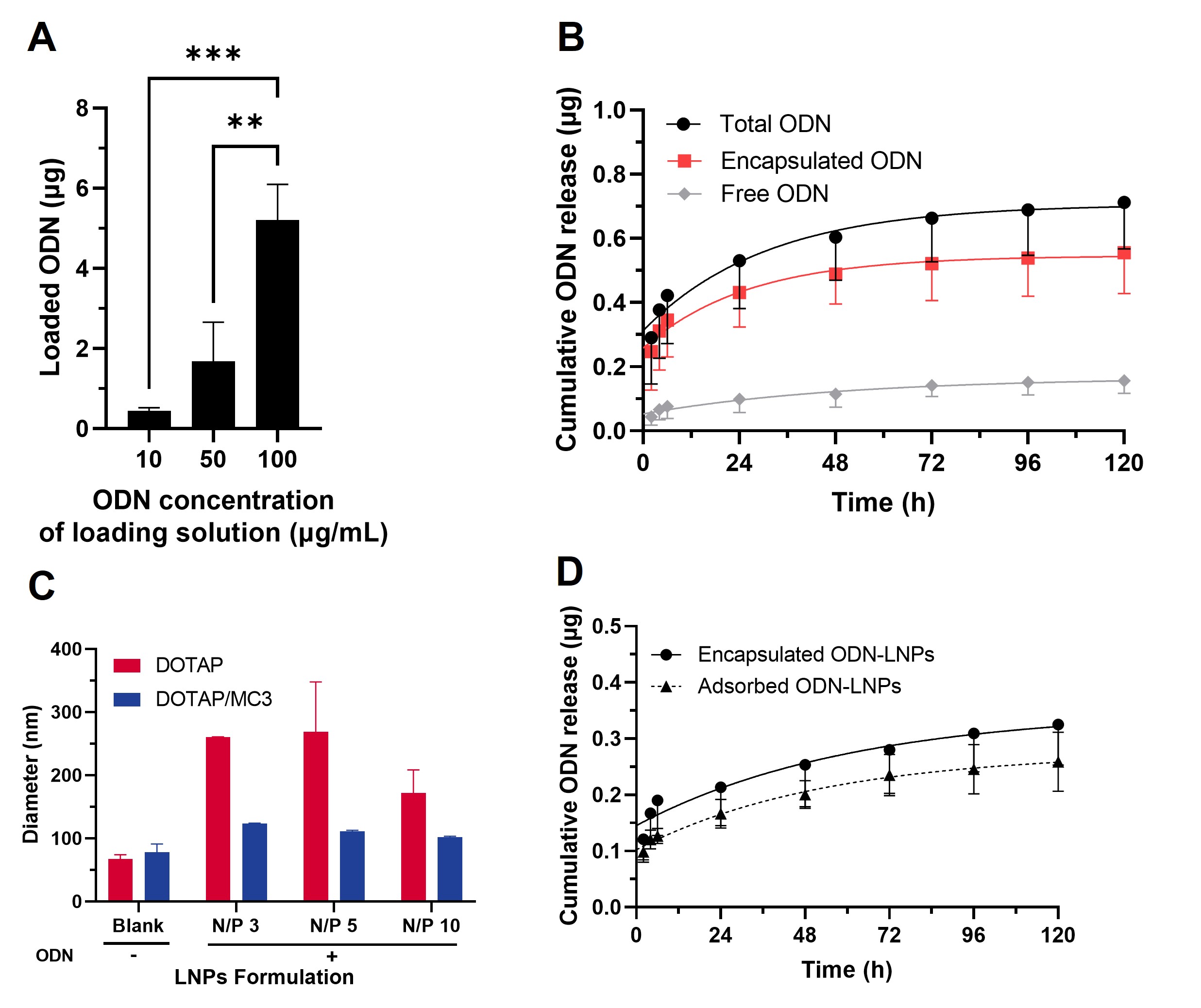 Figure 3. (A) ODN loading (μg) of encapsulated ODN-LNPs in granular hydrogel at varying ODN loading stock concentrations (μg/mL). (B) Release of total, encapsulated and free ODN from encapsulated ODN-LNPs in granular hydrogel at 100μg/mL ODN stock concentration, as quantified using the RiboGreen assay. (C) Diameter (nm) of LNPs prepared with DOTAP or DOTAP/ D-Lin-MC3-DMA cationic/ionizable lipids upon adsorption of ODN at varying N/P ratios. (D) Release of ODN from encapsulated DOTAP-LNPs or adsorbed DOTAP/ D-Lin-MC3-DMA-LNPs from granular hydrogel at 50μg/mL loading stock ODN concentration, as quantified using the RiboGreen assay.
Figure 3. (A) ODN loading (μg) of encapsulated ODN-LNPs in granular hydrogel at varying ODN loading stock concentrations (μg/mL). (B) Release of total, encapsulated and free ODN from encapsulated ODN-LNPs in granular hydrogel at 100μg/mL ODN stock concentration, as quantified using the RiboGreen assay. (C) Diameter (nm) of LNPs prepared with DOTAP or DOTAP/ D-Lin-MC3-DMA cationic/ionizable lipids upon adsorption of ODN at varying N/P ratios. (D) Release of ODN from encapsulated DOTAP-LNPs or adsorbed DOTAP/ D-Lin-MC3-DMA-LNPs from granular hydrogel at 50μg/mL loading stock ODN concentration, as quantified using the RiboGreen assay.